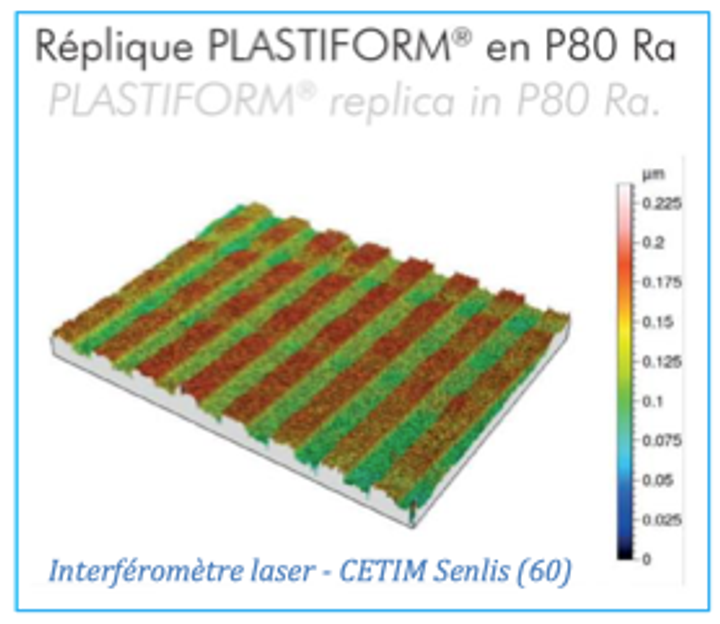
Plastiform P80 Ra, as its name suggests, is a product capable of copying the Ra roughness of a surface and reproducing it identically. This ability allows it to be used in cases where the surface to be measured is not accessible to the measuring instrument.
Table of Contents
Roughness with Plastiform
Definition
Roughness corresponds to the irregularities present on a surface due to level differences.
The Arithmetic Average Roughness, denoted Ra, is the arithmetic mean of the absolute values of the deviations of the profile within the reference section. In other words, it is the average difference between the peaks and valleys of the profile over a given measurement distance.
This Ra value is what can be obtained on P80 Ra using a contact roughness tester. Other characteristics (Rt, Rz, etc.) can only be obtained with non-contact surface measurement systems.
Replica Resolution
Resolution is the smallest absolute value that can be distinguished or identified by a measurement system on the replica.
Tests on subnanometric resolution optical systems (laser interferometer and scan) have shown a replica resolution of the order of 1 nanometer. This demonstrates that Plastiform products, and in this case P80 Ra, are capable of reproducing details of the order of nanometers on application surfaces.
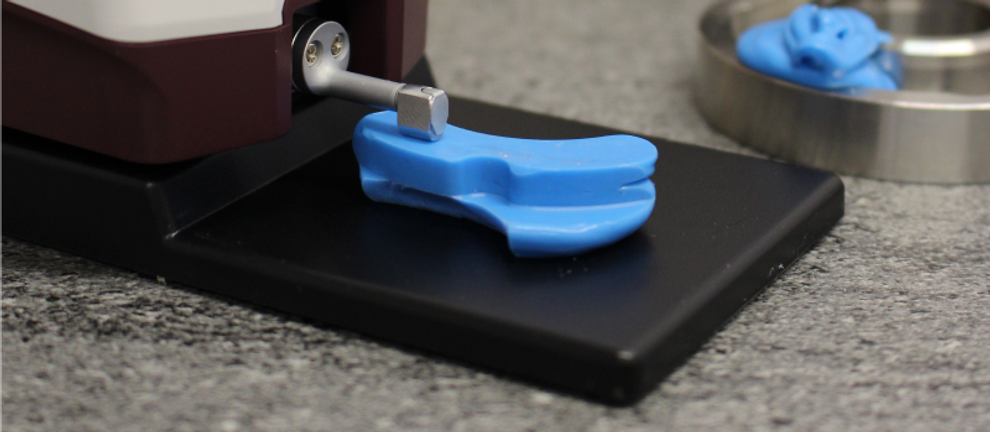
In general, it is recommended to use an optical measurement system to measure Plastiform replicas; however, contact measurement remains very precise if the proper procedure is followed.
Measurement Systems and Results
There are two main types of contact roughness testers: stylus roughness testers with and without skids. While both can be used for measurements on P80 Ra replicas, the best results are generally obtained with skidless roughness testers. These instruments allow obtaining tolerances of the order of +/- 0.1 µm.
For optimal precision, optical measurement systems (non-contact) are the most suitable. They allow measuring Ra roughness below 0.020 µm with great precision.
Methodology for Contact Measurement
This procedure has been developed with the help of multiple customer applications. It is the best method to obtain optimal results with a contact measurement device.
1. Clean the surface well
Before taking the replica, it is crucial to thoroughly clean the part using DN1 degreaser to avoid falsifying the roughness control. The surface must be perfectly clean, without any grease or oil residue. The presence of dust will also affect the quality of the replica.
2. Follow the instructions to take the impression
Measuring the roughness of a part requires rigorous application of Plastiform on the control surface. Refer to the instructions for a quality application.
P80 is a paste-like product that will not flow, so it can be applied to any type of surface.
However, be careful not to create air bubbles!
We recommend pressing the replica against the surface to be measured with a flat object to create a flat surface on top, but also to ensure good infiltration of the product into the micro-details of the surface.
In this way, you will obtain a polymerized replica that is easy to position under the stylus.
3. Wait 30 minutes After Polymerization
Once the P80 has polymerized, let it sit for about 30 minutes before starting the roughness measurement. This will allow the product to reach its final hardness of 80 Shore A.
This hardness is essential for an accurate measurement.
4. The measuring System Must Be Calibrated
Before taking the measurement on the P80 Ra replica, it is imperative to properly calibrate your measurement system.

We even advise testing the roughness tester on the replica of the roughness standard to verify compliance. To do this, take the replica of the roughness standard and compare the results obtained on the replica and on the standard.
5. Position the impression correctly
Place the replica so that the grooves are perpendicular to the direction of measurement and ensure it is stable and as flat as possible.
We recommend creating a “plate” on the back of the replica when making it (see point 2 above). The replica must also be well-held so that it does not move due to the friction of the stylus.
Do not hold the replica with your fingers, as this causes harmful micro-movements
6. Take the measurement
According to the standard, the profile must be measured over 5 different sections to obtain an average.
Additionally, since the stylus can slightly damage the surface of the replica, the measurement should not be taken twice in the same place.
Factors Influencing Measurement Results
When measuring surface roughness, several factors can impact the measurement result. And other factors come into play when it comes to a measurement on a replica. Here is a non-exhaustive list.
1. Environment
Temperature variations can influence the result of a roughness measurement. Air humidity can also affect the result of a measurement.
2. Human Factor and Measurement Strategy
The experience of the measurement technicians also has an impact on the measurement result. The choice of the measurement method or the appropriate probe is an important element for obtaining optimal results.
3. Measuring device
The choice of the most suitable measuring device determines whether the control will be easy or complex.
Some instruments are perfectly compatible with Plastiform replicas, while others will have more difficulties. This is why a prior test is always recommended to verify the compatibility of the equipment.
4. Object of measurement
The original surface, as well as the surface of the replica, must be perfectly clean, and the Plastiform replica must have reached its maximum final hardness (about 30 to 40 minutes after application).
It is also important to preserve the control surface of the replica as much as possible. Since it is not made of metal, it should not be scratched, rubbed, or twisted too strongly. It must be handled and positioned with care.
5. Ra Limit Value
When the Ra roughness of the surface is less than 0.4 µm, contact measurement becomes unsuitable.
Due to the low roughness, a deviation appears, leading to errors in interpreting the roughness tester.
Therefore, it is necessary to switch to an optical measurement instrument (non-contact) when the roughness being measured is less than or equal to 0.4 µm.