Metrology is a scientific discipline that includes all methods for obtaining measurements. Industrial Metrology is a branch of the discipline applied to the production sector.
In the industry, metrology is most often used to check dimensional conformity, it is a way of ensuring quality control.
Table of Contents
Industrial metrology and scientific metrology differences
This discipline was originally used to ensure the conformity of productions in the industrial sector.
It has since become popular in other sectors. There are many differences between industrial and scientific metrology:
- Industrial metrology is voluntarily implemented by the company in order to certify the conformity and the validity of its production. This approach meets global standards and allows the company to certify its know-how or the quality of its products.
- Industrial metrology is part of a quality assurance process. It is the company that decides which standards it wants to meet and is based on units defined internationally by scientific metrology.
Scientific metrology is dedicated to defining, developing and calibrating the units of measurement used.
Like all disciplines of science, it is subject to a consensus of the international scientific community.
The science of measurement is vast, so we recommend this article to get into the details.
Scope of the discipline for industry
Product compliance verification can be done at different times during the product’s life cycle.
Industrial metrology is mainly involved during the production of the product and during its use. We therefore distinguish two functions:
- Product conformity verification: during production, the controller ensures that the product conforms to the plan and meets the associated standards. It is a product validation process.
- Verification of product wear and tear: during use, the controller carries out regular checks to ensure that any alteration to the product does not affect its conformity. It is a process of risks anticipation.
Thus, verification by measurement is done in different ways and is carried out by production supervisors, usually the method and quality assurance departments.
The metrologist only applies the procedures defined by the company to determine the required measurements.
Difficulties encountered during measurements in the industrial metrology processes

Operators sometimes encounter difficulties in carrying out the requested measurements. Sometimes the parts do not adapt to the measuring instruments available to the company and the use of metrological laboratory machines is sometimes very expensive.
Quality control techniques then developed different procedures to allow measurements when they cannot be measured directly on the workpiece. Destructive testing and indirect testing in a remote location.
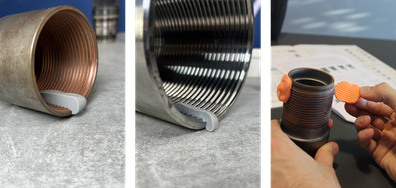
With impression taking techniques, it is possible to carry out delocalized indirect controls that are perfectly in line with the logic of industrial metrology.
Instead of destroying the part to measure it in pieces, the fingerprints copy the properties to be measured. It is then possible to take measurements directly on the replica.
At Plastiform, we develop products that seek to meet the challenges faced by small and medium-sized companies in the field of industrial metrology.
Although essential, this discipline can be very costly for growing companies. This is why we are trying to develop products that can meet all needs. Plastiforms can ensure the conformity of a product or to check its state of wear.
Indirect measures
Thanks to technologies such as Plastiform, the operator is able to copy with great precision the information contained in a part (dimensions, surface finish, roughness, etc.).
Measuring on a replica of the part allows you to avoid the destruction of the part (this is especially useful if your parts are expensive to machine or if they are large).
By performing the measurements via an intermediary, you carry out an indirect control of the part to be inspected.
Depending on the criteria imposed on you, you are therefore able to certify the conformity of your part!
Conclusion
Industrial metrology is a process that is very present in modern industry. It ensures the conformity of the products created and controls their state of wear throughout their life cycle.
Within quality control processes, metrology is essential to meet internationally recognized standards and certifications and it is important to be properly equipped to meet them.
If your controls seem complicated, expensive or even impossible, turn to outsourced indirect control techniques by using impression taking.
Plastiform provides you with a wide range of products that can be used for any type of indirect inspection, in particular Dimensional Inspections or Surface Quality Inspections.